Obsidian offers a very valuable accompaniment for conventional business intelligence tools, as it provides a 360º vision of IT services, allowing for analysis of the impact of IT services on business processes.
Although we often talk about business intelligence generically, it really encompasses two different, yet closely related concepts: business intelligence (BI) and business analytics (BA). However, an official definition has never been agreed upon. In fact, we could even say that there are as many definitions as there are experts working in the field. For many, BI is part of BA. For others, it is just the opposite. Some also believe them to be converging terms. Others see them as complimentary disciplines, or even complete opposites.
Business Intelligence vs Business Analytics
In an attempt to shed some light on the matter, we have outlined below our definition of these terms and how they relate to Obsidian:
The objective of business intelligence is to build data models using multiple sources. These models provide knowledge to help support decision-making processes.
The purpose of business analytics is to analyse the data models provided by business intelligence and apply statistical techniques and artificial intelligence. The objective is to understand the “why” behind the data, its distribution and forecasting.
Gartner’s Magic Quadrant for Analytics and Business Intelligence
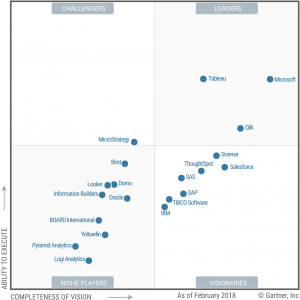
Magic Quadrant for Analytics and Business Intelligence Platforms.
Perhaps another difference between BI and BA is that the former is traditionally associated with the generation of models using multiple sources, the creation of dashboards and reports and their distribution across the organisation.
The world of BA, on the other hand, is more closely associated with the act of drawing conclusions from data models, applying multiple techniques Among these techniques are descriptive analytics, visual pattern recognition, predictive modelling, machine learning etc.
In fact, the world of analytics has popularized the concept of self-service analytics, where each user is provided with the necessary tools and data to complete their own analysis and obtain their own individual conclusions.
Through the years, the line dividing the two disciplines has become increasingly blurred. Now, virtually all tools present in the Gartner magic quadrant show characteristics belonging to both BI and BA disciplines.
Obsidian and business intelligence tools
So, according to the definitions above, Obsidian would be considered a specific type of BI for service management. It provides a holistic model of IT services and their impact on business.
To do this, it provides a service modelling methodology that gathers data both for real-time and historical analysis purposes. With this data, Obsidian’s objective is the real-time and historical monitoring of SLA fulfillment levels. Thus, the purpose of Obsidian is not analyzing data..
This model can be used as one of the sources for a classic BI tool in order to create a more complete model. Obsidian is the perfect complement for conventional business intelligence tools. It provides a 360º vision of IT services, allowing for analysis of the impact of IT services on business processes.
Obsidian with analysis and visualisation tools
In order to complete analysis, it is necessary to have a data model first. This model can be very simple and can be built using Excel or any other corporate tool. It can also be built using business intelligence models.
Obsidian provides a complete model for service management which would be impossible to natively build with analysis tools.
This means that Obsidian does not compete with analysis tools, as both are mutually beneficial.
This is what Obsidian does contribute to analysis tools:
- A data model for service level and SLA compliance. Analysis tools do not have a real-time calculation engine. Neither do they offer mechanisms for adding indicators for the generation of service level indicators using infrastructure and software metrics.
- An additional level of analysis. All the data added at the service level can be used by business analytics tools to analyse behaviors, detect patterns, etc. It can also be integrated with classic BI models and provide additional drill-down criteria of business data.
On the other hand, visual analytical functions incorporated within Obsidian are not comparable to those offered by commercial analysis platforms. It will always be useful to have a tool of this type in order to get the most out of the information provided by Obsidian.
Integration with Obsidian
Obsidian’s data model can be consulted from any BI/BA tool in mainly in two different ways:
- Using Obsidian’s REST webservice which facilitates information on service and component levels. It also facilitates the natural language processing of real-time indicators, reports and notifications.
- Directly accessing Obsidian’s MySQL database, whose relational model is documented in the administration manual.
Examples of integration with Business Intelligence and Analytics tools
Select any of the links below to see different examples of the integration of Obsidian with business intelligence and business analytics tools.
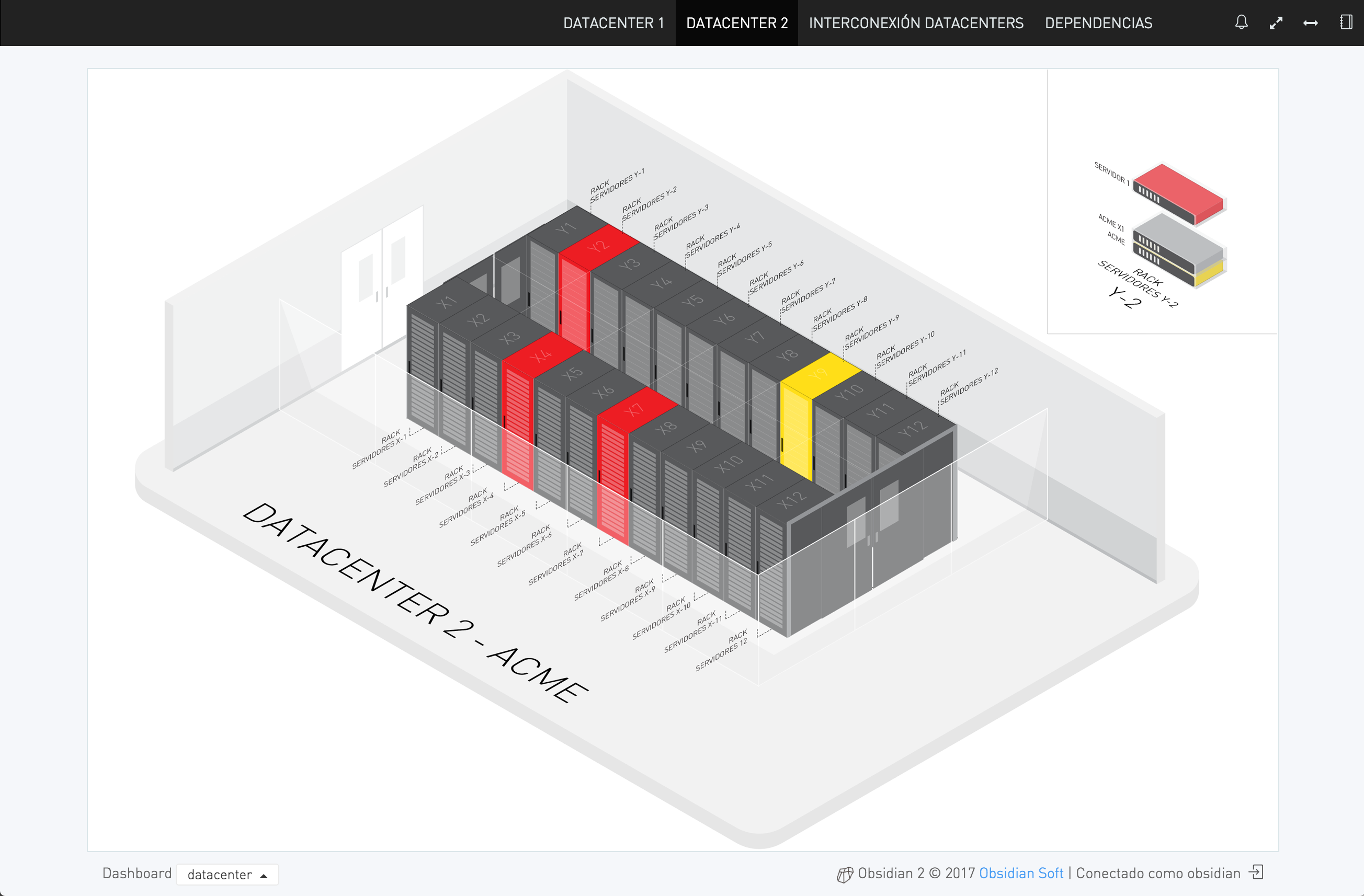
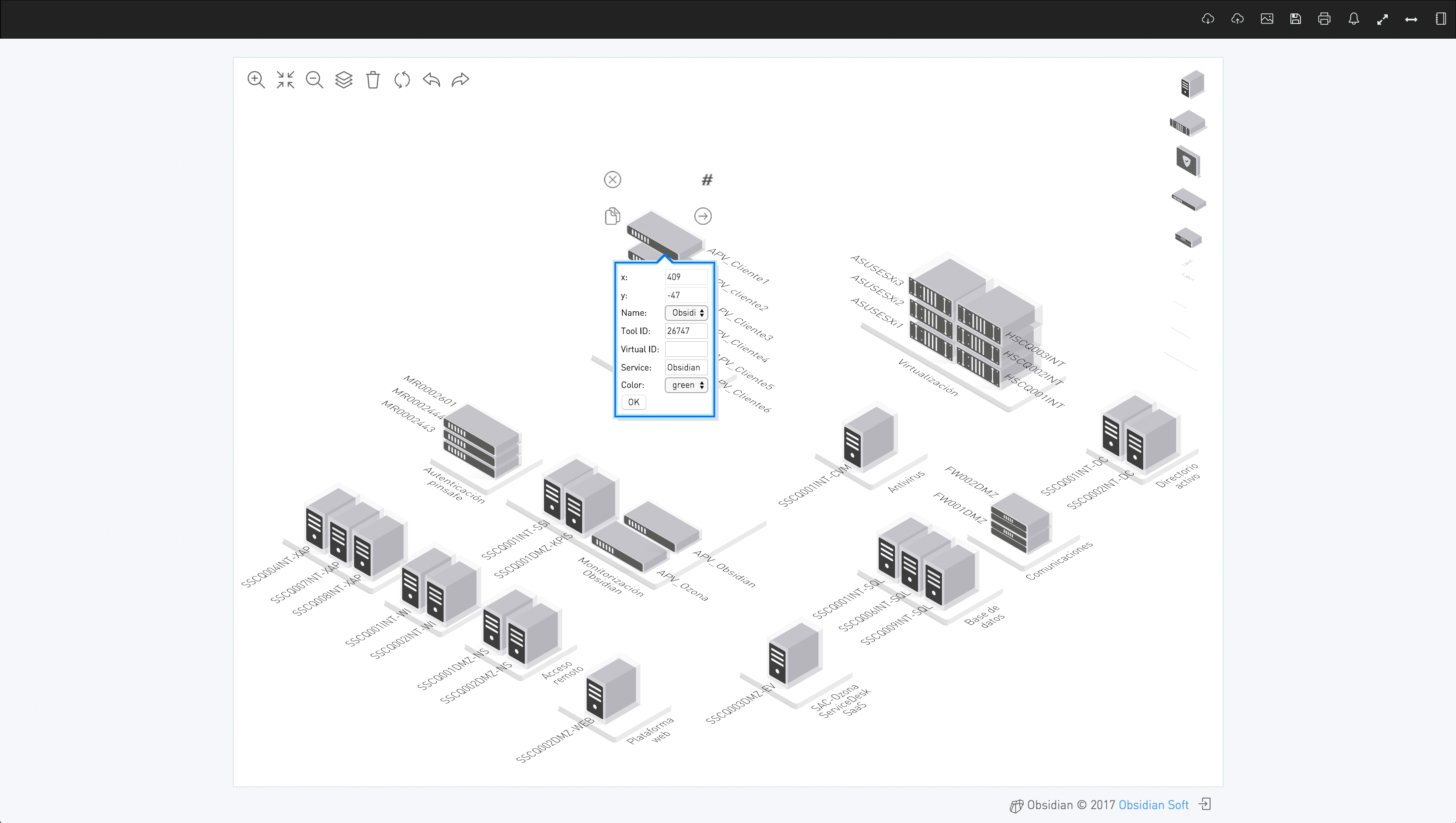
Datacenter Map
dashboard, dashboardEN, mapa, mapaENInfrastructure maps created using Obsidian’s online editor
dashboard, dashboardEN, mapa, mapaENFurther information
If you want more information about about business intelligence and business analytics or other features of our platform, please contact us via the attached form.
NOTE Only professional e-mail addresses are accepted. Requests from gmail, yahoo, hotmail, etc. accounts will not be processed.
The personal data collected via the form will be used to process your request. You may exercise your rights of access, rectification and cancellation by writing to Obsidian Soft, calle Méndez Álvaro, 20 · 18045 · Madrid.
You can also subscribe to our newsletter or to our YouTube channel, which currently has 1580 subscribers. You may also be interested in reading our blog, as well as the snews section of our website in order to find our more about Obsidian. Lastly, you can follow us on LinkedIn, Facebook and Twitter.